Gingivitis is a common dental problem that affects many people in the United States. It is a mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation, redness, and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can lead to more serious complications such as periodontitis, tooth loss, and increased risk of heart disease and diabetes. Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible and preventable with proper oral hygiene and dental care. In this blog post, we will explain what gingivitis is, what causes it, how to recognize its symptoms, how to treat it, and how to prevent it from recurring.
Table of Contents
What is Gingivitis?
It is the inflammation of the gingiva, which is the part of the gum that surrounds the base of the teeth. It is caused by the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth, which are sticky films of bacteria that feed on the sugars and starches in food. Plaque and tartar irritate the gums and cause them to become swollen, red, and prone to bleeding. It is usually painless and may not cause any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, if left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more severe form of gum disease that affects the bone and tissue that support the teeth. Periodontitis can cause permanent damage to the gums and teeth, leading to tooth loss and increased risk of infection and systemic diseases.
What Causes Gingivitis?
The main cause of gingivitis is poor oral hygiene, which allows plaque and tartar to build up on the teeth. However, there are other factors that can increase the risk of developing gingivitis, such as:
- Hormonal changes: During pregnancy, puberty, menopause, or menstrual cycles, hormonal fluctuations can make the gums more sensitive and susceptible to inflammation.
- Smoking or chewing tobacco: Tobacco use can impair the blood flow to the gums and reduce their ability to heal and fight infection. It can also stain the teeth and increase plaque formation.
- Diabetes: Individuals who have diabetes are more susceptible to developing infections, including gum disease. High blood sugar levels can also affect the health of the gums and teeth.
- Medications: Some medications can affect the saliva production or composition, leading to dry mouth or increased plaque formation. Some medications can also cause gum enlargement or overgrowth, which can make it harder to clean the teeth.
- Nutritional deficiencies: A lack of vitamin C or other essential nutrients can weaken the immune system and affect the health of the gums and teeth.
- Genetic factors: Some people may have a genetic predisposition to developing gum disease due to inherited traits or conditions.
- Other diseases or conditions: Some diseases or conditions that affect the immune system or cause inflammation can increase the risk of developing gum disease. These include HIV/AIDS, leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn’s disease, etc.
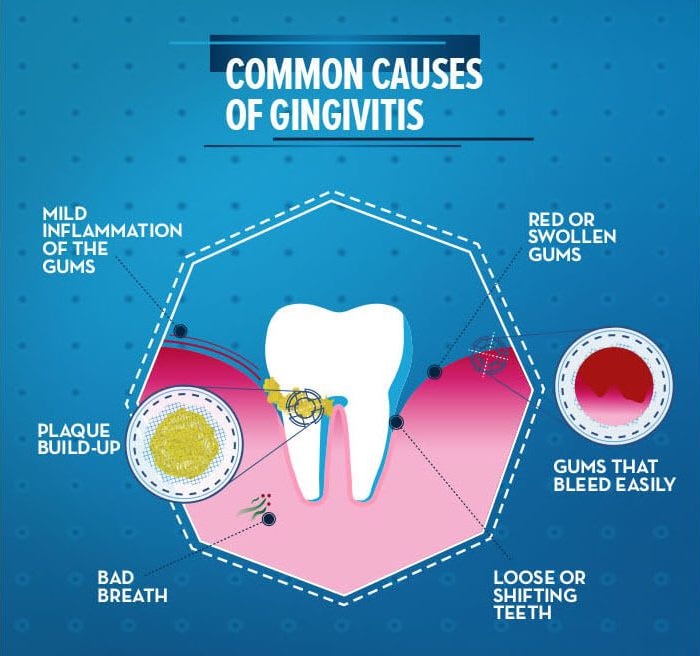
Gingivitis Symptoms
It may not cause any noticeable symptoms in its early stages. However, as it progresses, it may cause some signs and symptoms such as:
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Gums that readily bleed while brushing or flossing
- Bad breath that persists even after brushing or using mouthwash
- Gums that are receding, uncovering a greater portion of the tooth’s root
- Loose or shifting teeth
- Feeling tooth sensitivity or pain when you eat hot or cold foods
If you notice any of these symptoms, you should visit your dentist as soon as possible for a diagnosis and treatment.
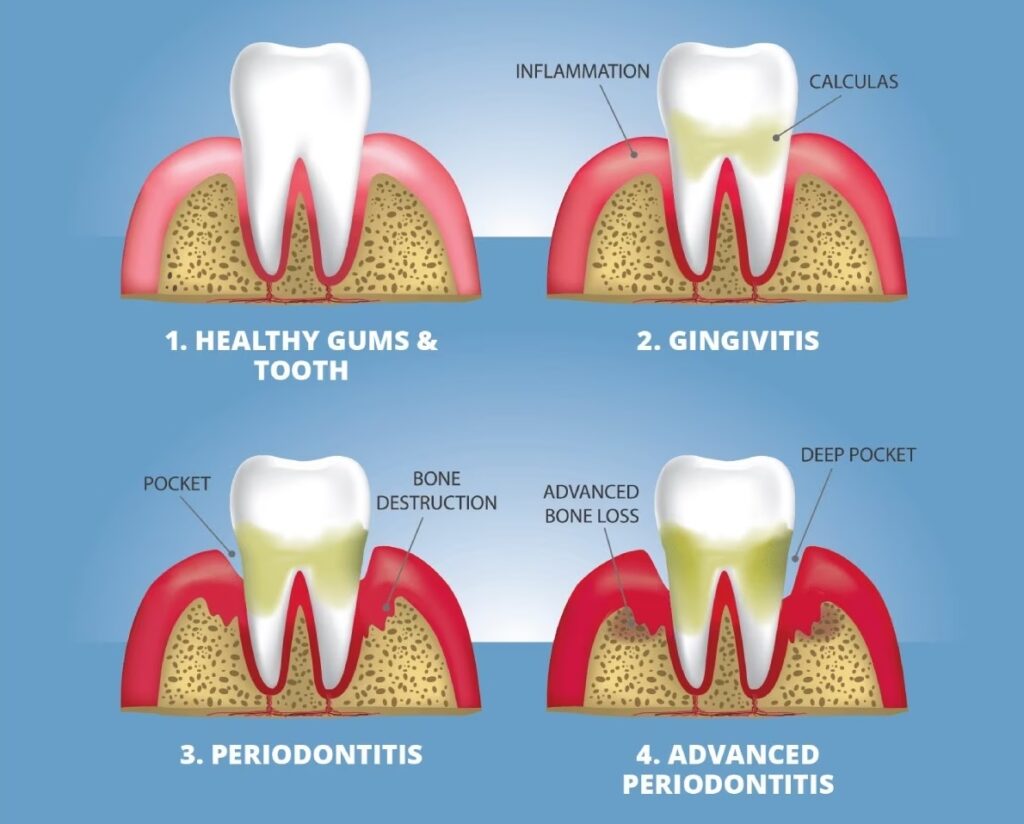
Gingivitis vs Periodontitis
Gingivitis and periodontitis are both forms of gum disease, but they differ in their severity and consequences. Gingivitis is a mild form of gum disease that affects only the superficial layer of the gums. It is reversible with proper oral hygiene and dental care. Periodontitis is a more severe form of gum disease that affects the deeper layers of the gums as well as the bone and tissue that support the teeth. It is irreversible and can cause permanent damage to the gums and teeth.
The main difference between gingivitis and periodontitis is the presence or absence of pockets between the gums and teeth. Pockets are spaces that form when the gums pull away from the teeth due to inflammation or infection. Pockets allow bacteria to accumulate and cause further damage to the gums and bone. In gingivitis, there are no pockets or they are shallow (less than 3 mm deep). In periodontitis, there are pockets that are deeper than 3 mm.
The treatment for gingivitis and periodontitis also differs depending on their severity. For gingivitis, regular dental cleanings and improved oral hygiene at home are usually enough to cure it. For periodontitis, more intensive dental procedures such as scaling and root planing (deep cleaning), flap surgery (gum surgery), bone grafting, or tissue regeneration may be required to treat it.
How to Get Rid of Gingivitis
The best way to get rid of gingivitis is to remove the plaque and tartar that cause it. This can be done by visiting your dentist for a professional dental cleaning and by improving your oral hygiene at home. Here are some tips on how to get rid of gingivitis:
- Make sure to brush your teeth two times a day with a toothbrush that has soft bristles and fluoride toothpaste. Brush for at least two minutes and make sure to reach all surfaces of your teeth, especially along the gum line.
- Floss your teeth once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and under your gum line. You can also use an interdental brush, a water flosser, or a dental pick to clean between your teeth.
- Rinse your mouth with an antiseptic mouthwash that contains chlorhexidine, cetylpyridinium chloride, or essential oils. These ingredients can help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation in your mouth. Adhere to the directions provided on the label, and avoid swallowing the mouthwash.
- Make it a habit to see your dentist for regular checkups and cleanings at least twice a year. Your dentist can remove plaque and tartar that you cannot remove at home and monitor your gum health. Your dentist may also recommend more frequent visits if you have gingivitis or other dental problems.
- If you currently smoke or use tobacco, it’s advisable to quit. Tobacco use can worsen gingivitis and increase the risk of developing periodontitis and other oral diseases.
- Eat a balanced diet that is rich in vitamin C and other nutrients that support your immune system and oral health. Avoid sugary foods and drinks that can feed the bacteria in your mouth and cause plaque formation.
- Stay well-hydrated by drinking ample water to help keep your mouth moist and wash away food particles and bacteria. Water also helps stimulate saliva production, which helps neutralize acids and protect your teeth and gums.

How to Cure Gingivitis
It is curable with proper oral hygiene and dental care. However, it may take some time for the symptoms to disappear completely. Depending on the severity of your gingivitis, it may take from a few days to a few weeks for your gums to heal and return to their normal color, shape, and texture. During this time, you should continue to follow the tips mentioned above on how to get rid of gingivitis. You should also avoid any habits or factors that can irritate your gums or cause further inflammation, such as:
- Brushing too vigorously or using a toothbrush with hard bristles
- Using toothpaste or mouthwash that contains alcohol or sodium lauryl sulfate
- Eating spicy, acidic, or crunchy foods that can scratch or burn your gums
- Drinking alcohol or caffeinated beverages that can dehydrate your mouth
- Stressing too much or not getting enough sleep
If you follow these tips consistently, you should be able to cure gingivitis in a week or less. However, if you notice no improvement or worsening of your symptoms after a week, you should consult your dentist for further evaluation and treatment. You may have a more advanced form of gum disease that requires more intensive dental procedures.
Is Gingivitis Contagious?
It is not contagious in the sense that you cannot catch it from someone else by kissing or sharing utensils. However, it is caused by bacteria that live in your mouth and can be transferred from one person to another through saliva. Therefore, if you have gingivitis, you may pass some of the bacteria that cause it to someone else through close contact. This does not mean that the other person will automatically develop gingivitis, as there are other factors that influence the development of gum disease, such as oral hygiene, genetics, diet, etc. However, it may increase their risk of developing gingivitis if they already have poor oral hygiene or other predisposing factors.
To prevent the transmission of bacteria that cause gingivitis, you should avoid sharing items that come into contact with your mouth, such as toothbrushes, cups, straws, spoons, etc. You should also avoid kissing someone who has gingivitis until their symptoms have cleared up. You should also practice good oral hygiene yourself to reduce the amount of bacteria in your mouth and prevent it from recurring.
How to Treat Gingivitis at Home
There are some home remedies that you can try to treat gingivitis at home. These remedies are not meant to replace professional dental care but rather to supplement it and provide some relief from the symptoms of gingivitis. Some of these home remedies include:
- Salt water rinse: Salt water has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties that can help reduce swelling and infection in your gums. Mix half a teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth with this solution multiple times a day.
Hydrogen peroxide rinse: Hydrogen peroxide is a natural bleaching agent that can help whiten your teeth and kill bacteria in your mouth. Dilute one part of 3% hydrogen peroxide with two parts of water and rinse your mouth with it once a day. Do not swallow the solution or use it more than once a day, as it may cause irritation or damage to your gums and teeth.
- Baking soda paste: Baking soda is a mild abrasive that can help remove plaque and stains from your teeth. It also helps neutralize acids and balance the pH level in your mouth. Mix one teaspoon of baking soda with a few drops of water to form a paste and apply it to your teeth and gums. Allow it to sit for a few minutes, then rinse it off with water. Do this once or twice a week to see results.
- Aloe vera gel: Aloe vera is a natural anti-inflammatory and healing agent that can help soothe and heal your gums. Apply some fresh aloe vera gel to your gums and massage it gently. Leave it on for 10 minutes and then rinse it off with water. Repeat this process twice daily until you see an improvement in your symptoms.
- Turmeric paste: Turmeric is a spice that has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help reduce swelling and infection in your gums. It also helps prevent plaque formation and tooth decay. Mix one teaspoon of turmeric powder with enough water to form a paste and apply it to your gums. Leave it on for 10 minutes and then rinse it off with water. Repeat this process twice daily until you see an improvement in your symptoms.
- Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil is an essential oil that has antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties that can help fight bacteria and inflammation in your gums. Add a few drops of tea tree oil to a glass of warm water and rinse your mouth with it twice a day. You can also add a drop of tea tree oil to your toothpaste and brush your teeth with it. Do not swallow the oil or use it undiluted, as it may cause irritation or allergic reactions.
These home remedies can help treat gingivitis at home, but they are not substitutes for professional dental care. You should always consult your dentist before using any of these remedies, especially if you have any medical conditions or allergies. You should also continue to follow the tips on how to get rid of gingivitis mentioned above.

Is Gingivitis Curable?
It is curable with proper oral hygiene and dental care. However, you need to be consistent and diligent in following the tips on how to get rid of gingivitis mentioned above. You also need to visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings, as well as for any dental procedures that may be required to treat any underlying problems that may cause gingivitis. If you neglect your oral health or ignore the symptoms of gingivitis, you may develop periodontitis, which is not curable and can cause serious complications.
Therefore, the best way to cure gingivitis is to prevent it from happening in the first place. By maintaining good oral hygiene, eating a healthy diet, quitting smoking, managing stress, and visiting your dentist regularly, you can keep your gums healthy and avoid gum disease.
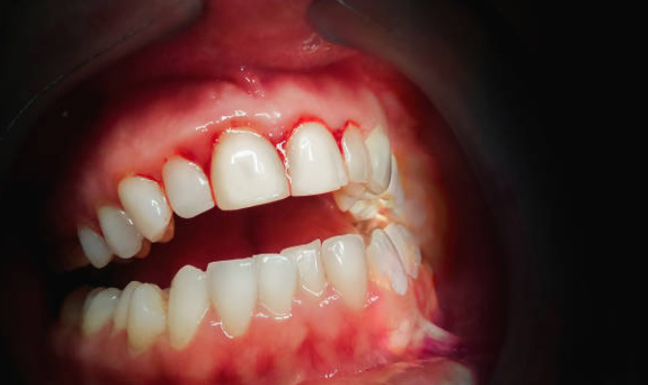
What Does Gingivitis Look Like?
It can affect different people in different ways, depending on the severity and duration of the condition. However, there are some common signs and symptoms that can help you identify gingivitis, such as:
- Redness: Your gums may appear red or pink instead of their normal pale color.
- Swelling: Your gums may look puffy or swollen due to inflammation.
- Bleeding: Your gums may bleed easily when you brush or floss your teeth, or even when you eat or touch them.
- Recession: Your gums may pull away from your teeth, exposing more of the tooth root or creating gaps between the teeth.
- Bad breath: You may have persistent bad breath or an unpleasant taste in your mouth due to the bacteria in your mouth.
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, you should visit your dentist as soon as possible for a diagnosis and treatment.

How to Cure Gingivitis in a Week
If you have mild gingivitis, you may be able to cure it in a week by following the tips on how to get rid of gingivitis mentioned above. However, this depends on several factors, such as:
- The severity of your gingivitis: The more severe your gingivitis is, the longer it will take to heal.
- The duration of your gingivitis: The longer you have had gingivitis, the more damage it may have caused to your gums and teeth.
- The cause of your gingivitis: If your gingivitis is caused by an underlying problem such as diabetes, hormonal changes, medications, etc., you may need to address that problem first before curing gingivitis.
- Your oral hygiene habits: The more diligent you are in brushing, flossing, rinsing, and visiting your dentist, the faster you will cure gingivitis.
- Your lifestyle habits: The more you avoid smoking, drinking, eating sugary foods, stressing, etc., the faster you will cure gingivitis.
Therefore, there is no definitive answer to how long it will take to cure gingivitis, as it varies from person to person. However, if you follow the tips on how to get rid of gingivitis consistently and visit your dentist regularly, you should be able to cure it in a week or less. However, if you notice no improvement or worsening of your symptoms after a week, you should consult your dentist for further evaluation and treatment.
Also read about “Tooth Abscess: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments”, click here.
Conclusion
Gingivitis is a common dental problem that can affect anyone at any age. It is a mild form of gum disease that causes inflammation, redness, and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, it can lead to more serious complications such as periodontitis, tooth loss, and increased risk of heart disease and diabetes. Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible and preventable with proper oral hygiene and dental care. By following the tips on how to get rid of gingivitis mentioned in this blog post, you can cure it in a week or less and keep your gums healthy and happy. However, if you have any doubts or concerns about your gum health, you should always visit your dentist for a professional diagnosis and treatment. Remember, your gums are the foundation of your smile, so take good care of them!
We hope this article has helped you learn more about Gingivitis. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us below. We would love to hear from you! 😊
1 thought on “Gingivitis: A Complete Guide to Preventing and Treating Gum Disease in 2025”